The latest figures from Tianhong Asset Management show that the AUM (asset under management) of Yu’ebao deposits, the currency market fund which is co-launched by Alibaba and Tianhong on 13 June, 2013, has rocketed from June 13th to November 14th, 2013, from 0 to CNY100B. Now Yu’ebao is the largest fund in China leveraging it's enormous Taobao, T-mall and Alipay customer base.
The latest figures from Tianhong Asset Management show that the AUM (asset under management) of Yu’ebao deposits, the currency market fund which is co-launched by Alibaba and Tianhong on 13 June, 2013, has rocketed from June 13th to November 14th, 2013, from 0 to CNY100B. Now Yu’ebao is the largest fund in China leveraging it's enormous Taobao, T-mall and Alipay customer base.
The success story of Yu’ebao has not only encouraged the Chinese IT giants and online payment providers to enter the asset management market, but also is a worry to the traditional asset management firms. Currently, most public funds in China sell their products on their own websites or choose to cooperate with the online platforms to sell their products. Asset managers do recognise the benefit of selling funds online including low cost and convenience, but struggle as they simply just do not have the customer base of Alibaba/Alipay.
| Date | 13 June | 30 June | 9 Sept | 14 Nov |
| AUM (CNYB) | 0 | 6.6 | 55.65 | 100 |
The U.S. Government Shutdown and Its Impact
The shutdown of the U.S. government ended as the two U.S. political came to an agreement to delay the decision to January-February of 2014. This means that the global market instability will likely still be on-going until the beginning of next year. This also means that the U.S. market may not be as lucrative and attractive as before, as critical decisions regarding the debt ceiling and government funding are still not solved.
It is important to figure out the impacts of the incident on Chinese economy, as the U.S. and China are the world’s number 1 and 2 economies with strong ties. The index trends in East Asia, oil consumptions and imports by China, and geo-political status of China are all important aspects to consider to understand the impact.
Market Change after the End of Shutdown
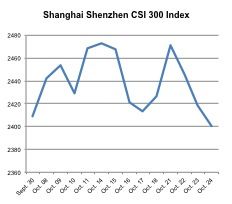
The Chinese stock index fell right after the announcement of the end of the government shutdown, while other East Asian and Southeast Asian market indexes rose. Although, it is hasty to conclude that China had served as a ‘refugee market’ or as an alternative to the U.S. market just from that factor, one could draw certain implications that people were shifting their investments in and out of the US / China as a the appeal of each market shifted.
U.S. – China Relations from multiple angles
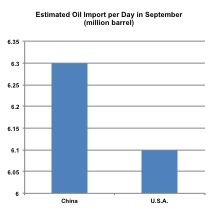
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s latest report, China surpassed the U.S. in terms of oil imports in September, due to oil consumption surpassing production. Part of the reason behind this is that the U.S. has been decreasing the total import of crude oil – China is replacing the U.S. demand. If this trend continues, and the decrease of oil price also continues, China will benefit from the outcome by stabilizing the export production cost, but at the same time become more susceptible to the oil price. The economic ties with the U.S. has to be a factor here, as crude oil imports to China are used for the refined oil products and the production of manufacturing goods that go to other nations around the world. Since the U.S. is the biggest individual nation in terms of absorbing Chinese exports, the susceptibility will only be counterbalanced when Chinese exports are sold with minimum hindrance.
 The ultimate factor, however, is the sovereign debt of the U.S. held by China. In 2011 China already became the top
The ultimate factor, however, is the sovereign debt of the U.S. held by China. In 2011 China already became the top 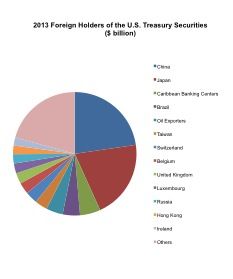 U.S. government debt holder, accounting for the 8 percent of total U.S. public debt. Even in percentage terms the figure is very high. As long as the U.S. has the economic power to pay back the interest and return the principal for the matured bonds, both the U.S. and China have little to worry about. However, the current talks on debt ceiling and budget talk have changed the atmosphere. For the U.S. when a single country has such high debt in time of financial instability is one more thing to worry about. For China, it is now holding a potential time bomb – even though the chance of the U.S. default is very low, the lessened credibility of the U.S. government bonds means the future investment channel is narrowed. The portfolio of Chinese government requires changes, and the currently-held debt needs to be reevaluated in terms of the possibility of return. Chinese government needs to diversify its risk coming from the U.S. instability.
U.S. government debt holder, accounting for the 8 percent of total U.S. public debt. Even in percentage terms the figure is very high. As long as the U.S. has the economic power to pay back the interest and return the principal for the matured bonds, both the U.S. and China have little to worry about. However, the current talks on debt ceiling and budget talk have changed the atmosphere. For the U.S. when a single country has such high debt in time of financial instability is one more thing to worry about. For China, it is now holding a potential time bomb – even though the chance of the U.S. default is very low, the lessened credibility of the U.S. government bonds means the future investment channel is narrowed. The portfolio of Chinese government requires changes, and the currently-held debt needs to be reevaluated in terms of the possibility of return. Chinese government needs to diversify its risk coming from the U.S. instability.
Geo-Political Movements of China
As China is a well-known politically stable country with one party system, at the moment of the U.S. instability, the characteristic is clearly a benefit to China. However, in modern economy, nations maintain close political and economic relationship. This means the U.S. instability will have a likely negative impact on China.
Then the question we have to ask is how much impact the U.S. instability will have on Chinese economic growth. It is possible that China would not be able to enjoy high growth rates it used to for the next 3 to 4 months, as the U.S. is one of the top 3 markets for China. If the U.S. market is not able to consume as many goods as it used to be due to the instability, China will face further reduced exports. These exports alone represent about one fourth of the total GDP, and the net export is about one eighth of the total GDP. Therefore, if China export to the U.S. slows by a considerable amount because of the instability, the consequence for China will not be great. Whether it was done to counter such consequence is not clear, but the president Xi and the premier Li’s meetings with the leaders of ASEAN nations can be seen as a type of insurance for China. This will not only increase the geo-political strength of China, thus further stabilizing regional politics, but also create more economic ties with the region to divert exports and investment channels.
However, so far the “magnet of economy” is still at the U.S. market, and the power of the magnet is very strong. In other words, the determinant of global market trends is the U.S. and that fact will be the key to the Chinese economic prospects. The geo-political factor of Southeast Asia is not yet strong enough to counterbalance the current instability formed in the U.S. market and politics.
Possible “Next Steps” for China
The Chinese market may not show a sudden change, but the prolonged instability will certainly diminish the economic strength that China has been showing for a couple of decades. This means China has to prepare for certain changes that could affect its future growth. Before the shutdown, there had been worries on the U.S. Federal Reserve’s (the Fed) tapering on quantitative easing. Now the concern on the U.S. budget and debt ceiling talks adds more worries to developing nations. Nations including China will have to worry about whether to focus on development as they have been doing, or to focus on stabilizing the domestic economy and strengthening the weak links within their own economy. As the government shutdown caused economic instability, the Fed will most likely continue its quantitative easing to secure economic conditions for now. That does not mean the instability of the Fed’s tapering is removed, because it is like the status of the U.S. budget talk: the quantitative easing is only a temporary solution.
Even though China has a huge domestic market, in time of economic instability, the driving force of economy is hard to find. Export is not going to help China go through this hard time as the whole world is suffering together, and domestic consumption growth is still up in the air. In September, Chinese exports faced an unexpected year on year drop. When looking at the income of Chinese people, that does not seem to help increase domestic consumption. Other possible economic boosts such as government spending or investment are still viable options, but the question is “how long and how much the Chinese government and corporates are willing to put money into it?”
Not only that, China also faces the question of liberalization of the market. China has shown strong commitment to liberalize and open up further to the global market, especially in financial and trade sectors. The recent interest rate reform and Shanghai Free Trade Zone were two of the examples that have shown Chinese commitment through action. Since there is instability in the global market, the economy will not be as energetic enough as Chinese government expected it to be for its liberalization process. This means that China can cut its effort down to open up the market and slow down the pace of economic expansion. This could be a problem if the investors around the world, who think China will still show strong growth, find out about the policy changes in China. Even if the investors have anticipated the slowdown, the actual impact of Chinese slowdown will be massive, considering the size of Chinese economy.
Also, Chinese government external debt has increased significantly in recent 10 years, more than tripling since 2002. China has funded many projects through debt, and if the economic expansion diminishes, it will adversely affect the debt / deficit balance in China. The Chinese government will have a harder time borrowing money at the same interest rate, and have a harder time paying back debts as the profit from projects diminishes due to the domestic economic slowdown and the global economic recession. Then the government projects will have to face the new consequence of either reduction in size or complete shutdown, and overall investment and financial inflow will diminish, which can be a vicious cycle. Even though Chinese government will put extra effort to prevent such cycle, the diminishing trend is inevitable.
However, It could be a good opportunity for China in terms of restructuring its domestic economic design. Rather than focusing too much on expansion and growth, China can restructure its economy through strengthening small and medium enterprises, or increase the consumers’ purchasing power. The latter might be a harder task for China, as it includes increased welfare, restructuring of wage systems, and implementation of social safe-nets – this is even hard for other developed nations. However, strengthening SMEs is achievable through several banking reforms that would either guide banks to give more access for SMEs to capital, or allow more commercial and private banks to open up and target SMEs as major customers.
China’s Possible Direction
Overall, China is facing a key decision-making period as the U.S. economic power is in question due to the prolonged debt ceiling and budget talks. With strong economic ties to the U.S., China faces trade-offs: whether to continue its economic expansion policies or to restructure its economy. It will be detrimental for China to continue the expansion as there will be no country to be able to support such moves economically. Especially when the world’s number 1 economy is unstable, the scenario is highly unlikely. Hence China will stay low and withhold any further reforms that can tip off the balance. Possible policies could be to strengthen domestic markets, but even then, the implementation of policies will not come fast, as the instability from the U.S. is not predicted beforehand. Nevertheless, this can be the valid option for China at this moment – the restructuring is an inevitable process for a developing nation.
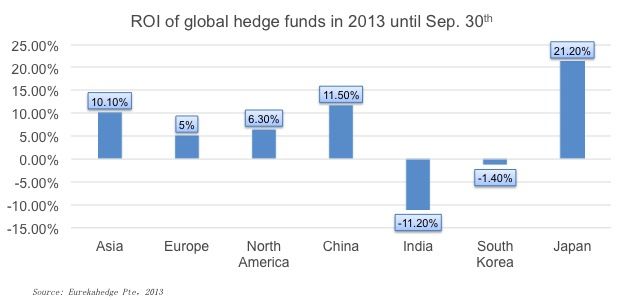
Recent figures from Eurekahedge showed that the general ROI of Asian hedge funds (10.1%) surpassed that of North American hedge funds (6.3%) and Europe hedge funds (5%) for the first 3 quarters of 2013. However, among Asian countries, Japanese and Chinese hedge funds have experienced relatively high ROI while Indian and South Korean hedge funds suffered from negative ROI. Market analysts suggested that, the high ROI from China is because of the sustained and relatively fast economic growth, while the high ROI for Japan is for the massive economic stimulation.
Cash is always king and no more so than in China. Traditionally a very cash-based market with many High Net Worth Individuals (HNWI) skeptical of having someone else manage their money, wealth management got off to a slow start in China. It started with the establishment of few foreign private banking such as Citi Bank, UBS, and HSBC in China in 2006. In 2007, Bank of China was the first Chinese bank that established a private banking department in Beijing and Shanghai.
Business was slow initially for both foreign and domestic banks. Trust was a key factor – many HNWIs were not comfortable with someone else managing their money, much less a foreign bank, but the sophistication of services offered was also very low. Even today, the private banking business mainly provides consulting services for asset allocation and very little forward planning. Most banks push particular products rather than tailored financial plans that take into account not just a person or family’s financial situation, but their future life events.
Although wealth management is still in a nascent stage, the HNWI population in China has increased dramatically, reaching 700,000 by the end of 2012. In addition, the total AUM in Chinese private banks was 573.6 billion yuan in 2008, but is over 2 trillion yuan today. With this growing trend, we see the huge potential in the wealth management sector in the near future.
China’s large banks also see this opportunity and are focusing more and more on wealth management. The wealth management business does not only bring significant intermediate business income, but also provides an opportunity for organisations to re-structure their retail banking business. This has become especially important as it appears that regulators are finally going to reform interest rates. More flexible interest rates will mean that banks will face increased competition and be able to rely less and less on traditional spread income – this is where higher margin wealth management products and services can help.
Nevertheless, Chinese banks still need a long time to build trust with their customers. In western countries, many private banks already have more than a hundred years of history. Will Chinese banks accomplish the same in less than 90 years?
|
Total Customers |
Customer Growth Rate |
AUM (Billion RMB) |
Minimum Amount (Million RMB) |
|
|
BOC |
40000+ |
- |
450 |
8 |
|
ABC |
35000 |
12.90% |
396 |
8 |
|
ICBC |
26000+ |
18.18% |
473.2 |
8 |
|
CCB |
- |
18.82% |
- |
10 |
|
CMB |
19518 |
18.34% |
434.2 |
10 |
Source: Bank Annual Reports, 2013
According to the figures from the Securities Association of China, the assets under management and revenue earned by Chinese securities companies asset management businesses has grown dramatically from the 1h 2011 to the 1h 2013. The total AUM in the 1h 2013 is about 13.75 times of the figure in the 1h 2011, which reflects the thriving of client asset management business of securities companies in China.
One reason for that for the dramatic expansion is the demand from clients. As China has a growing number of high-net-worth individuals and the investment options are relatively narrow compared to western countries, asset management business provided by local securities companies are thought to be a good choice. Market analysts estimated that the figures will keep growing exponentially for the following few years; at least the current market is far below saturation.
|
Client asset management business of Chinese securities companies CNYbn |
|||||
|
1h 2011 |
2h 2011 |
1h 2012 |
2h 2012 |
1h 2013 |
|
|
Revenue earned by securities companies |
0.898 |
1.215 |
1.044 |
1.632 |
2.88 |
|
Total AUM |
248.673 |
281.868 |
480.207 |
1890 |
3420 |
Source: Securities Association of China, 2011-2013
The US Federal Reserve (Fed) announcement that it will continue the program of quantitative easing (QE) boosted the Asian stock market, but many now worry that this is only a temporary fix.
According to the latest figure from the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SHSE) the trading volume of ETFs in SHSE increased dramatically from the beginning of 2012 to August 2013. It is quite obvious from the data that 2013 is far larger than the figure in 2012. The lowest point from this period is April 2012, when the ETF trading volume was only CNY16.232bn; The peak was in June, 2013, with a trading volume of CNY68.712bn, which is over 4 times compared to the figure at the bottom in 2012. Besides, the aggregate trading volume for the previous 8 months is CNY449.687bn, which is far larger than the whole year figure of 2012 of CNY302.658bn. As ETFs are very important components in investors’ portfolio, we estimate that there will be more ETFs launched and the trading volume could be larger as we close out 2013 and move into 2014.

China initiated its asset securitization program in 2005 for securities companies. However, after the subprime mortgage crisis swept over the globe, regulators in China temporarily stopped the program because although it provides liquidity to markets, securitization also comes with significant risks. In 2012, the asset securitization program was initiated once again with permission from the state council and the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC). Regulations were changed to allow for more types of asset securitization and the threshold for securities companies to enter was lowered. The following report provides a summary regarding the participants, regulations and current conditions within China’s asset securitization markets.
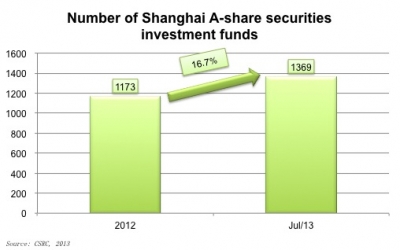
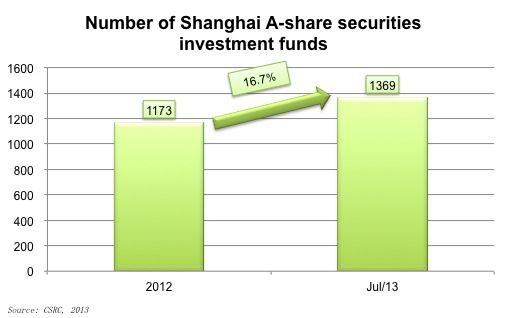
According to the latest figures from the CSRC, the number of securities investment funds for A-share market increased from 1,173 at the end of 2012 to 1,369 by the end of July, 2013. The structure of investors in Shanghai's A-share market has long been an interesting phenomenon for Chinese A-share market as individual investors comprise the major market force, which is thought to be a sign of a immature capital market. Currently, as the number of institutional investors is growing fast, it indicates to some extent that Chinese capital market is gradually developing towards the direction of a mature capital market, at least from the investor structure perspective.
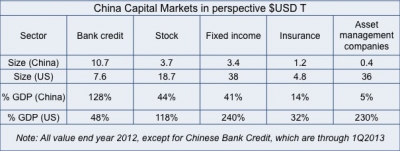
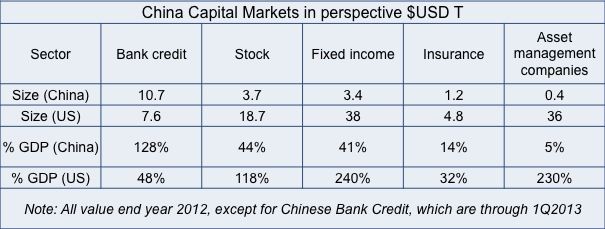
According to a 2013 publication by Goldman Sachs, there are still major differences between US and Chinese capital markets. The most prominent difference is that capital markets in the US are much larger than China’s in all sectors except for bank credit as shown in the figure below.
The Chinese banking credit sector has expanded in recent years which is now at 128% of China’s GDP compared with 48% in the US. Thus the Chinese economy is highly dependent on bank credit, which can be dangerous for the country in the coming years.
In other sectors, there are large gaps between the size of Chinese and US capital markets with the former still lagging behind the latter. Thus, there are many opportunities for China to develop its stock and fixed income markets, along with its insurance and asset management industries. Among these, the asset management industry seems to have the greatest growth potential.
On August 6, 2013, Chinese securities companies received ‘the notice of preparing the initiating stock options full simulating trading works’ sent by the Shanghai Stock Exchange. This information implies that SHSE is already fully prepared for the launching of stock options. Although there is no clear timetable for launching the stock options, it is likely that they will appear in Chinese capital markets in 2013 or 2014.
Throughout the history of capital markets in China, public listings, or IPOs in the Chinese A-share market have been suspended 8 times; we are currently in the 8th suspension period. The modern Chinese stock market is only about 23 years old and of that, IPOs have been suspended for nearly four and a half years, which makes up almost 20% of the market's history. There is still no actual timetable to reopen the IPO market, but according to some market information, it could be possible at some time in August or September, 2013.
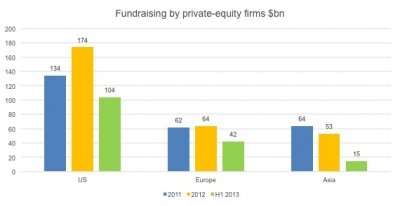
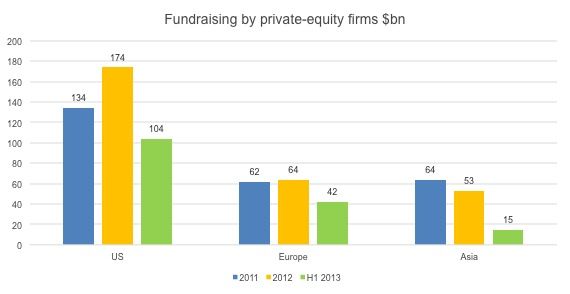
According to The Wall Street Journal, the fundraising of PE funds in Asia continued to drop in the first half of 2013. Compared to the US and European markets, the amount of funds that Asian private equity funds raised was the smallest among the three regions, while the percentage decline is the largest. The slowing Chinese economy is thought to be one of the biggest reasons for the decline in fundraising figures as well as the IPO suspension in China; only US$16 billion in public listings were completed in the first half of 2013.
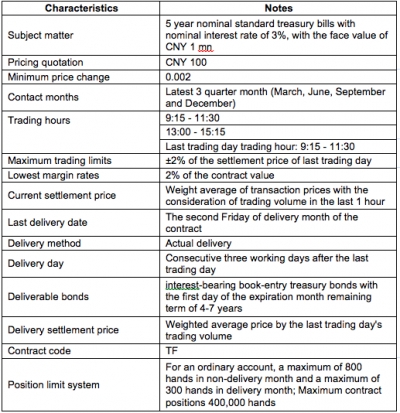
On 4 July, 2013, The China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) announced that the state council of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) had approved the Treasury bond futures’ return to trading, specifically on the China Financial Futures Exchange (CFFE). Currently, the T-bond futures are under the final preparation stage and it will take approximately two months for this preparation period before they officially are released and start trading. So the most likely time for T-bond futures to be released is in early September.
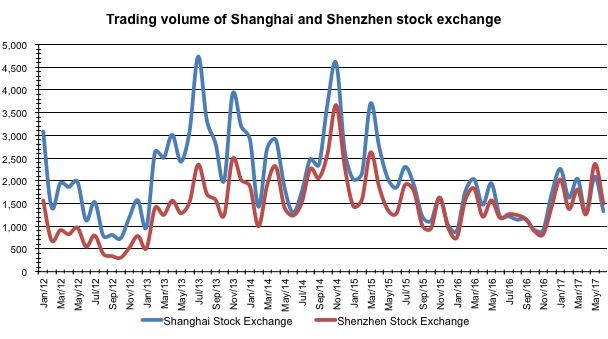
As seen from the chart below, the trading volume of Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges since August, 2011, the trading volume has fluctuated in a relatively low level, compared to the previous few years’ performance. We see this being a result of retail investors' lost confidence in a stock market that hasn't performed well recently, or at least not to the same levels as a few years ago.
This may be very temporary however as a number of the recent Chinese economic announcements and regulatory changes will likely have impact on the country as a whole and more specifically in the financial sector.
Watch this space.
The latest figures showed that in the first 6 months of 2013, the amount of FDI in China increased to US$61.98bn, a 4.9% increase compared to the first 6 months in 2012. Although the future of Chinese economy is under the threat of slower GDP growth, the figure illustrates that foreign investors are still interested in China as an investment destination.
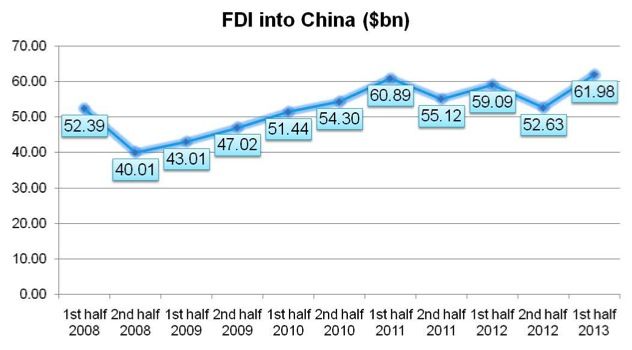 The latest figure showed that in the first 6 month, 2013, the amount of FDI in China increased to $61.98bn, a 4.9% increase compared to the first 6 months in 2012. . Although the future of Chinese economy is under the treat of slower down GDP growth rate, the figure illustrated that the foreign investors’ passion of investing in China remained at a high level in the first half of 2013.
The latest figure showed that in the first 6 month, 2013, the amount of FDI in China increased to $61.98bn, a 4.9% increase compared to the first 6 months in 2012. . Although the future of Chinese economy is under the treat of slower down GDP growth rate, the figure illustrated that the foreign investors’ passion of investing in China remained at a high level in the first half of 2013.
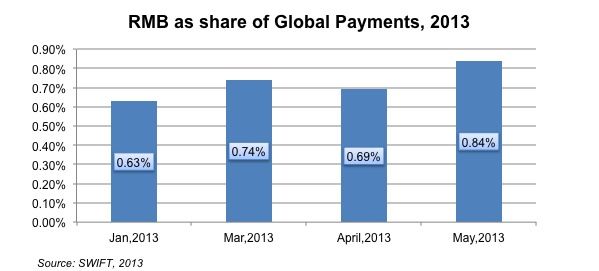
According to SWIFT (the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication), the Chinese Yuan (or RMB)'s share of global payments hit a new record high of 0.84% in May 2013, after the total value of yuan payment around the world increased sharply by 24% last month, compared with the average growth rate of 1.9% across other currencies. SWIFT also pointed out that China yuan is still the 13th most-used currency in the international trade. The growing demand for RMB settlement will continue to increase the use of yuan in future.
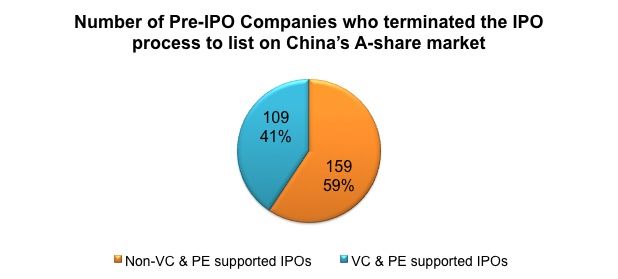
Based on CSRC’s data, about 268 firms queuing for IPO in A-share markets chose to quit the IPO process up until 31 May, 2013. 109 of these firms are supported by local VCs and PEs, which take about 41% of the total number of the firms who applied for IPOs in A-share markets. About RMB 8.45 bn investments from local VCs and PEs are locked into these pre-IPO firms, which is challenging for the VC and PE firms who might have been expecting an exit.
The tough supervision of the CSRC is one of the main reasons pre-IPO firms have left the process and only very few meet the standards and of those who did, the worry is that many have cooperated with local stock investment institutions to fake their financial performances to get them listed.
A few weeks ago, we looked at the growth of wealth management in China – a big aspect of wealth management is the Trust industry, which we look at today.
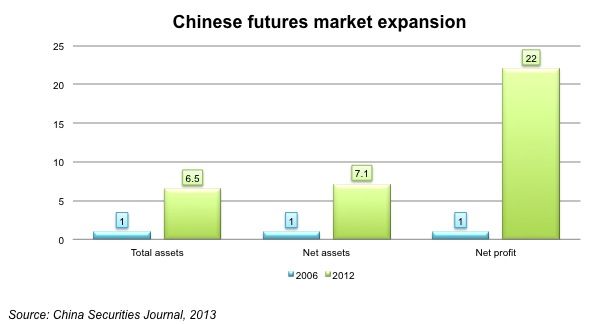
Across multiple metrics, the Chinese futures market grew rapidly from 2006 to 2012. Total assets have grown by 6.5 times over the 6 years, net assets 7 fold and net profit growth by nearly 22 times in 2012 compared to 2006. So it is quite clear that Chinese futures industry is growing at a high speed during the past few years and it is highly likely to expand even faster due to the opening up of the markets.
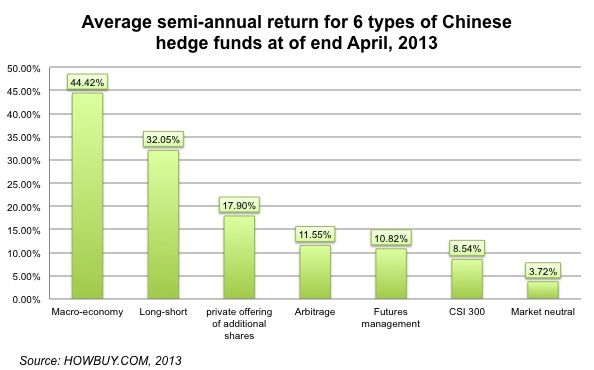
Based on the recent half-year performance of hedge funds, it appears that the average performance of all types of hedge funds outperformed the market return significantly with macro-economic hedge funds ranked first in returns from November of 2012 to the end of April of 2013.
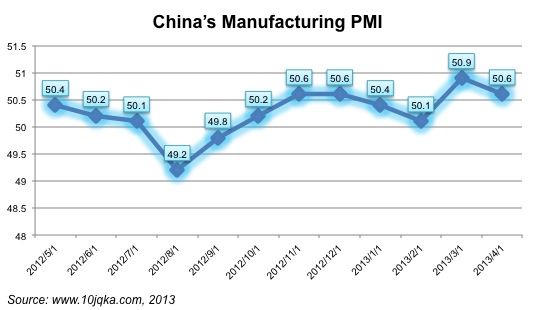
The latest Chinese manufacturing PMI is 50.6, declining by 0.3 point from March. From May 2012 to April 2013, this PMI figure has hovered the important line of 50 which is the watershed between economic growth and shrinkage. It signals that the growth of Chinese manufacturing economy is still fluctuating, largely because of the transformation and reformation of Chinese manufacturing industries during this period. The trend is expected to continue in the future so we will likely see continued fluctuations.
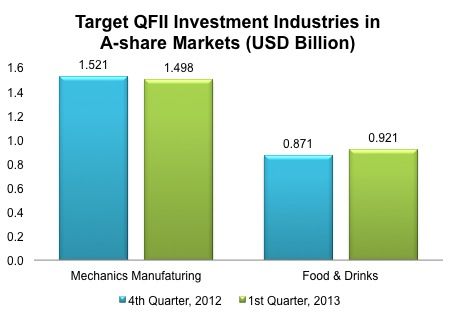
There are two main sub-industry categories that QFIIs seem to be investing in in China's A-Share market: the mechanics and food & drink manufacturing industries. During the first quarter of 2013, there was a slight decline of 1.55% in the QFII shareholdings in the mechanics manufacturing industry and a 5.78% increase in the food & drink industry.
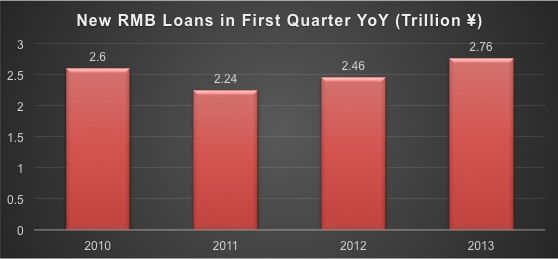
According to the PBOC, the value of new RMB loans in the first quarter of 2013 are at a three-year high. In the first quarter of 2013, the new lending is 2.76 trillion yuan, growing by 13%, compared with 2.46 trillion yuan in the same period of 2012. It signals that the financing demands in the market start are increasing and analysts believe the total new loans will reach 9 trillion yuan in 2013. More interestingly, among the newly increased loans, 30% of the loans are long-term loans, showing a sign of a strong economic rebound in China.
Wealth management refers to a type of financial analysis, financial planning and management service that banks provide to high net worth individuals. Banks have the obligation to return certain profit by managing customers' funds in an agreed period of time.
The trust industry is currently the fastest growing segment in China's asset management industry so far in 2013. In Q4 2012, the total trust AUM was about US$1.195 trillion. At the end of Q1 2013, this number had reached about US$1.395 trillion representing a growth rate of about 16.7%. That growth rate is actually faster than the growth rate of bank loans / deposits, market growth of the securities market, bonds, funds and insurance industry.

In order to facilitate the RMB’s cross-border settlement and promote the global use of the RMB, China’s central bank (the PBOC) is now building an international payment system called as CIPS (The China International Payment System). This CIPS is expected to take one or two years to launch and will make cross-border RMB trade settlement more efficient and safer.
Kapronasia's latest report Trading China - A Look at the Issues and Opportunities in China's Capital Markets is now available in the research reports section of the Kapronasia website. The report, sponsored by Equinix, is a detailed look at the challenges and opportunities in China's capital markets. The report is free, but does require registration to download. For more information on the report, please look in the research reports section of the website above.
The Hedge Fund Association, in conjunction with Bloomberg, hosted the HFA - Bloomberg Shanghai Hedge Fund Panel Discussion: International Hedge Funds and Direct Investment in China, in Shanghai on January 5th, 2013. During the event, three experts shared their insight into the challenges and opportunities in China’s hedge fund industry in 2013. I had the opportunity to attend on behalf of Kapronasia and summarized some of my conclusions from the event here:
Margin trading is an important part of financial markets, especially for derivatives although the use of margin trading is still somewhat controversial in certain markets. In China, margin trading is relatively new and the phenomenon and behaviors observed in the markets from the use of margin trading are quite different from those of western markets. In order to better understand the markets, its worth taking some time to analyze the differences and provide suggestions to utilize the opportunities from the development of Chinese margin trading market development.
More...
In the past we haven’t spent too much time looking at the development of China’s financial futures market, but if you were to ask any China capital markets observer what some of the most important reforms of the past few years included, the introduction of the financial futures market would be one of them.
The CSRC’s latest figures show that 57 funds obtained QFII (Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor) licenses in the first 10 months of 2012, far more than any previous year since the program’s inception in 2003. This is a positive signal that foreign investors are more keen to invest in China. Moreover, on Nov. 14th, 2012, Chinese regulators decided to expand the quota by 200 billion yuan to specifically attract RQFII investments; it is predicted that the quota will soon be used up and likely regulators will continue to increase the quota amount.
Shanghai has been authorized to become the first pilot city for a new RMB cross-border program – RQFLP (Qualified Foreign Limited Partner, RQFLP) which means offshore RMB can be raised and used for private equity investments in the Mainland. Following traditional FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) and RQFII (RMB Qualified Foreign Institutional Investors), RQFLP has become a new channel for the backflow of offshore RMB. Bank of Shanghai and the Hong Kong subsidiary of Haitong Securities (one of biggest securities in mainland China) have signed a memorandum of cooperation to be the first to issue RQFLP products in Hong Kong. The total quota is about 1 billion RMB. Bank of Shanghai will provide custody services and Haitong securities will take charge of the design and issuance of the RQFLP products in Hong Kong. After being raised in Hong Kong, these offshore RMB will enter into Shanghai for private equity investments.

Earlier this week, Burberry announced lower than expected earnings which largely disappointed and somewhat scared markets. Their slowdown is global, but a key challenge was declining luxury spend from Chinese consumers – which is seen by many as a bellwether for the rest of a general industry slowdown. We’ve talked about luxury spending in China in the past, but it’s worth considering the implications of a potential slowdown in the luxury industry and the implications if the slowdown is indeed an indicator of a shift in the habits of China’s wealthy.